Introduction
Do Rats Bite People: Rats biting people may elicit a shiver down the spine, conjuring images of unsanitary creatures lurking in the shadows. Rats, though often seen as pests, are intriguing creatures with a complex relationship with humans. While it is not a common occurrence, instances of rats biting people do happen, and understanding the factors behind these incidents is essential. By shedding light on this subject, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge to navigate human-rat interactions and mitigate any potential risks associated with these encounters.
Rats, as small mammals, have played significant roles in history, both as vectors of disease and as subjects of scientific study. Their association with plagues and unsanitary conditions has made them a source of fear and fascination throughout human history. To dispel misconceptions and delve into the nuances of rat behavior and interactions with humans.
The potential risks they pose, and how to prevent such encounters. By shedding light on this subject, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge to navigate human-rat interactions and mitigate any potential risks associated with these encounters. So, let’s peer into the world of rats and unravel the mysteries behind their occasional and sometimes unexpected interactions with humans.
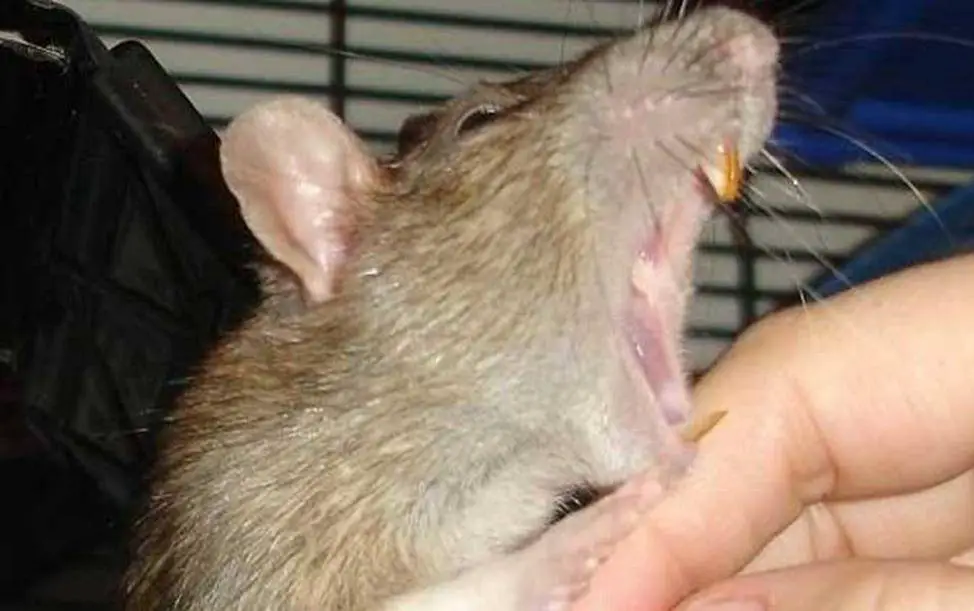
Do rats bite sleeping humans?
Wild rats will bite when handled or when people attempt to feed them by hand, as they are not accustomed to human contact. Nocturnal creatures have been known to bite sleeping people, especially children and infants, on exposed body parts.
Wild rats bite sleeping humans, particularly children and infants, on exposed body parts such as fingers, hands, toes, and the face. Rats are nocturnal creatures that may venture into human living spaces in search of food during the night. If a rat encounters a sleeping person and perceives them as a potential source of food, it may bite in an attempt to obtain sustenance.
Incidents are relatively rare, and wild rats generally avoid human contact. If there is a rat infestation in or near a home, the risk of such encounters can increase. To prevent rats from biting sleeping individuals, secure food sources, seal entry points, and consider professional pest control. Keeping sleeping areas clean and free of food crumbs can help reduce the attraction of rats to sleeping quarters.
What happens if a rat bites a human?
Rat bites usually look like a small, single puncture wound or a number of small cuts. They also tend to bleed and cause painful swelling. If the bite becomes infected, you might also notice some pus.
Pain and Swelling: Rat bites can be painful and often result in swelling around the bite area. The bite typically looks like a small, single puncture wound or multiple small cuts. The pain and swelling are usually the immediate effects and may persist for some time.
Bleeding: Rat bites can bleed due to the sharpness of their teeth. The bleeding may not be severe, but it can be noticeable.
Infection: If the bite breaks the skin, bacteria from the rat’s mouth can enter the wound and potentially lead to an infection. Signs of infection may include increased pain, redness, warmth around the bite area, and the presence of pus.
Transmission of Diseases: Bacterial infections, rats can carry and transmit diseases through their bites. While rat-bite fever is one such example, it’s essential to be aware of other potential diseases that rats might carry.
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to rat saliva or proteins in rat dander, leading to an allergic reaction. Symptoms range from mild itching and swelling to severe reactions, with anaphylaxis being rare from rat bites.
What happens if you corner a rat?
Rats are wild animals. Like all wild animals they may attack you if cornered or trapped. Try not to corner rats, because they could bite you in an attempt to escape. Basically, if you provoke them, there is a chance they will turn on you and attack.
Biting: When cornered or feeling trapped, rats may resort to biting as a means of self-defense. Their sharp incisors can inflict painful bites, and if the rat carries diseases, there’s a risk of disease transmission through the bite.
Scratching: Rats may also scratch when cornered, using their sharp claws to try and escape or defend themselves.
Agitation and Fear: Cornered rats are likely to exhibit signs of stress, fear, and agitation. They may vocalize, hiss, or make other defensive noises. Their primary goal will be to find an escape route and avoid confrontation.
Attempting to Flee: Rats are generally more interested in escaping from a perceived threat than in attacking. If you corner a rat, it will likely make every effort to find a way out of the situation.
Why are people scared of rats?
Media and everyday life commonly associate mice and rats with negative elements. It is common for mice and rats to be portrayed as carriers of disease, and pests that have strong connections to contamination and dirty places. These negative associations may cause a phobia to arise.
Disease Transmission: Rats have been associated with transmitting various diseases, including bubonic plague and leptospirosis. Historical outbreaks of these diseases, often attributed to rats, have fueled fear of these animals as disease carriers.
Filth and Contamination: Rats are often found in unsanitary environments such as sewers and garbage dumps, reinforcing the perception of them as dirty animals. Their association with filth and contamination can evoke disgust and fear.
Media Portrayals: Movies, literature, and other forms of media have frequently depicted rats as menacing and disease-spreading creatures. These portrayals reinforce negative stereotypes and can lead to fear.
Instinctual Fear: Humans have evolved with a natural instinct to be cautious around animals that could potentially carry diseases or pose a threat. This instinctual fear of animals like rats may have an evolutionary basis in survival.
Phobias: A traumatic experience or conditioned response can trigger the development of specific phobias, such as musophobia (fear of mice and rats), in some individuals.
Urban Environments: In urban areas, people often associate rats with pest infestations in homes and businesses, heightening their fear of these animals as unwanted intruders.
Size and Appearance: The appearance of rats, with their long tails and sharp teeth, can be unsettling to some people. Their rapid movements and nocturnal behavior can also contribute to fear.
How hard can a rat bite you?
They discovered that rats bite with an average pressure of about 1 pound. You read the right 1 pound of pressure. Gophers were almost identical, but squirrels were relative brutes, weighing in at nearly 3 pounds of bite force.
Rat bites are relatively low in terms of bite force compared to some other animals. Studies have shown that rats typically bite with an average pressure of about 1 pound of force. This is relatively mild compared to some other rodents and animals. For example, squirrels can exert nearly 3 pounds of bite force, making them relatively stronger biters in comparison to rats.
The strength of a rat’s bite can still cause pain and injury, especially if the bite breaks the skin. The risk associated with a rat bite goes beyond just the force of the bite, it includes the potential transmission of diseases or the risk of infection, which can be more significant concerns.
While a rat’s bite may not be exceptionally forceful, it’s crucial to treat any rat bite seriously by cleaning and disinfecting the wound, seeking medical attention if necessary, and taking preventive measures to avoid rat bites in the first place by minimizing contact with wild rats and practicing proper rodent control in and around living spaces.
Would a rat attack a human?
Rats are generally not aggressive towards humans and will only attack if they feel threatened or cornered. There have been cases of rats biting people, especially children. Rat bites can be dangerous, as they can transmit diseases such as rabies, leptospirosis, and tetanus.
Feeling Trapped: If a rat feels cornered or unable to escape, it may resort to biting as a defensive measure.
Protecting Young: Mother rats may become protective of their young and may bite if they perceive a threat to their offspring.
Attempting to Handle or Capture: Trying to handle or capture a wild rat, especially without experience or proper precautions, can lead to defensive behavior and a potential bite.
Food-Related Incidents: Rats bite when they attempt to steal food or perceive a threat to their food source.
While rats themselves are not typically carriers of rabies, they can carry other diseases like leptospirosis and can transmit them through their bites. Any animal bite, including a rat bite, can put bacteria into the wound, which can lead to infections like tetanus.
Why does my rat bite my feet?
Aggressive bites happen where a rat is attempting to establish its position as the more dominant in the relationship. It is more common where rats are going through a lot of changes in hierarchy or environment so the rat in question is feeling unsettled or under threat.
Exploration: Rats are naturally curious creatures, and they use their mouths to explore their environment. When a rat nibbles or lightly bites your feet, it may be trying to investigate and interact with you.
Playfulness: Rats are social animals that enjoy play, and nibbling on your feet may be a form of play or interaction from their perspective.
Communication: Rats use a combination of body language, vocalizations, and tactile interactions to communicate. Light nibbling on your feet might be their way of trying to get your attention or express their feelings.
Taste and Scent: Rats have an acute sense of smell and taste, and they may be sampling the scent or taste of your skin, particularly if you’ve recently applied lotion or have a scent that piques their curiosity.
Hierarchy and Dominance: In some cases, rats may exhibit territorial behavior or try to assert dominance. If a rat feels threatened or is adjusting to changes in its environment or social hierarchy, it may engage in nipping as a way to establish boundaries.
What diseases do rats carry?
Diseases Spread by Rodents
- Hantavirus.
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome.
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome.
- Lassa Fever.
- Leptospirosis.
- Lujo Hemorrhagic Fever.
- Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis (LCM)
- Monkeypox.
Hantavirus: Hantaviruses are a group of viruses that can cause Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome HPS. Infected rodents, including rats, transmit these viruses to humans through contact with their urine, feces, or saliva. HPS can be a severe respiratory illness.
Leptospirosis: The bacterium Leptospira, found in the urine of infected rodents, causes leptospirosis. Humans can become infected through contact with contaminated water or soil, or through direct contact with infected animals. It can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe organ failure.
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis LCM: LCM is a viral infection that is typically transmitted to humans through contact with the urine, droppings, saliva, or nesting materials of infected rodents, including rats. It can cause flu-like symptoms and, in severe cases, can affect the central nervous system.
Rat-Bite Fever: Rat-bite fever is a bacterial infection that can be transmitted to humans through a rat bite or contact with rat urine or saliva. Symptoms can include fever, joint pain, and skin rash.
Plague: While rare, rats can carry the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which causes the plague. Fleas that infest rats can transmit this bacterium to humans. Plague can cause severe illness and has historically been responsible for major pandemics.
Salmonella: Rats can carry Salmonella bacteria, which can contaminate food and surfaces through their feces. Ingesting food or water contaminated with Salmonella can lead to gastrointestinal illness.
Eosinophilic Meningitis: This is a rare disease caused by rat lungworm parasites. Humans can become infected by consuming contaminated food or water. It can lead to inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Lassa Fever: Although more commonly associated with other rodents, Lassa fever can be transmitted to humans through contact with rat urine or droppings. It is a viral illness with symptoms ranging from mild to severe.

Conclusion
Rats bite people is a complex one, and has shed light on the various factors at play. While it is true that rats are capable of biting humans, these incidents are relatively rare and are often a result of specific circumstances, such as feeling threatened or cornered. To recognize that not all rats are aggressive, and many can coexist with humans without posing a threat. we can create a safer and more harmonious coexistence between humans and these often misunderstood creatures.
Understanding the behaviors and habits of rats, as well as implementing preventive measures, can significantly reduce the likelihood of rat-human conflicts and potential bites. Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment, sealing entry points to homes and buildings, and responsibly managing food waste are essential steps in rat control.while it do have the capacity to rate bite the people, a proactive approach to rat management and education about their behavior can help minimize such occurrences.
Fostering a broader understanding of rats beyond their negative stereotypes can lead to more humane approaches to managing rat populations. This may include implementing non-lethal methods of rodent control and promoting coexistence in urban and rural environments. By taking these measures, we can create a safer and more harmonious coexistence between humans and these often misunderstood creatures.





No Comments