Introduction
What To Feed A Ferret With Insulinoma: Ferrets, those playful and curious little creatures, have long been cherished as unique and endearing pets. However, like all animals, they can face health challenges that require special attention and care. One such health concern that afflicts many ferrets is insulinoma, a condition that affects their pancreas and blood sugar levels. Insulinoma in ferrets can be a serious and life-threatening condition, but with the right approach, you can help manage it effectively. One crucial aspect of managing insulinoma in ferrets is their diet. Insulinoma is a condition where the pancreas overproduces insulin, leading to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). This can cause a range of symptoms, including lethargy, weakness, tremors, seizures, and in severe cases, it can even be fatal.
To mitigate these effects and improve the quality of life for ferrets with insulinoma, it is essential to pay special attention to their nutrition. The nuances of feeding a ferrets snow with insulinoma. We will choose the types of food that are suitable, those that should be avoided, and the overall dietary considerations that can make a significant difference in managing this condition. We’ll delve into the role of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in a ferret’s diet and how they can be balanced to help stabilize blood sugar levels. The feeding frequency, portion sizes, and supplementation, all of which are critical aspects of caring for a ferret with insulinoma.
Ferret-friendly foods and recipes that can be tailored to meet the specific nutritional needs of a ferret battling insulinoma. Navigating a ferret’s dietary requirements can be challenging, especially when managing a chronic condition, so our goal is to equip you with the tools necessary to ensure your ferret’s well-being. You will have a comprehensive understanding of how to get the best possible nutrition for your ferret with insulinoma, helping them lead a happier and healthier life despite their condition. So, let’s embark on this journey to discover the secrets of feeding a ferret with insulinoma and nurturing them back to vitality.
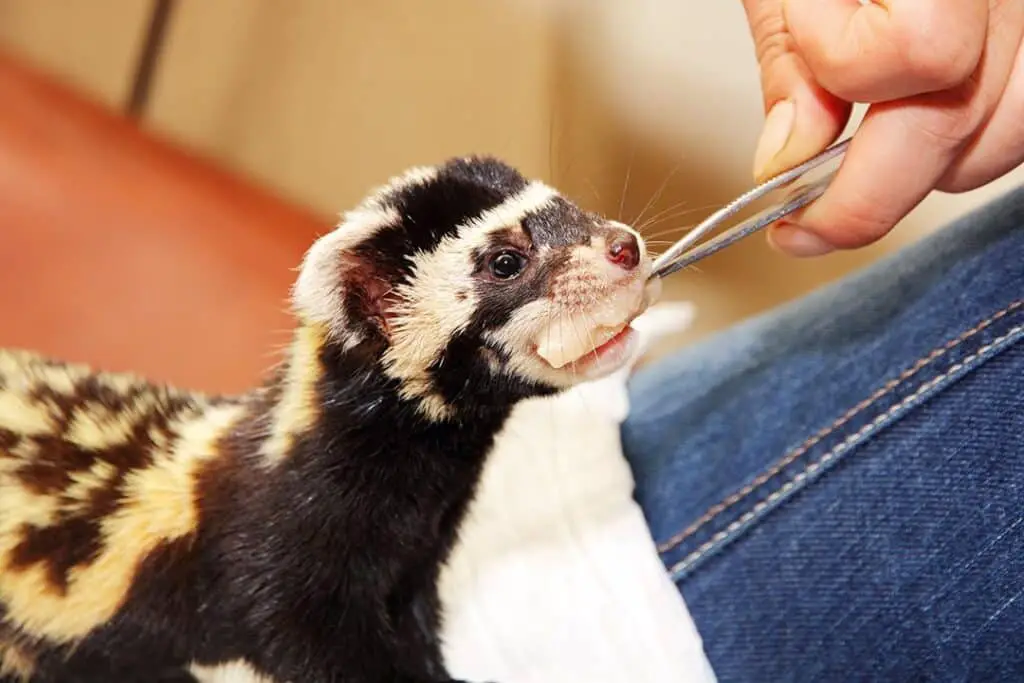

What do you give a ferret with insulinoma?
Most ferrets with insulinoma will need to take the steroid prednisolone which helps increase blood glucose concentrations. Unfortunately, this medication does not prevent the continued growth of the tumor.
The foundation of a ferret’s diet, especially when dealing with insulinoma, should be high-quality ferret food. Look for products that list meat, poultry, or fish as the primary ingredient. Ferrets are obligate carnivores, meaning their diet should be rich in animal-based proteins. Avoid foods with excessive carbohydrates, sugars, or fillers, as they can exacerbate blood sugar fluctuations.
Proteins are essential for ferrets, particularly those with insulinoma. They help maintain steady blood sugar levels and provide energy. Opt for meat-based protein sources such as chicken, turkey, and lamb. You can also provide high-protein treats like freeze-dried chicken or turkey as occasional rewards.
Carbohydrates should be minimized in a ferret’s diet, as they can cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Steer clear of foods with ingredients like corn, wheat, and soy. Some commercial ferret foods contain a small amount of carbohydrates, but it’s crucial to choose those with the lowest levels.
Healthy fats are another valuable component of a ferret’s diet. Incorporate fats from sources like fish oil or flaxseed oil to help maintain overall health. Avoid excessive fat intake, as it can lead to obesity, which is detrimental for ferrets with insulinoma.
What can you eat with insulinoma?
Aim for 8 small meals throughout the day to maintain blood sugar levels. Include a protein food at each meal or snack. Protein causes the meal to digest slower and helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Try lean meats, poultry, fish, reduced fat cheeses, soy foods, peanut butter, nuts or seeds.
Lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes, should be a staple in your diet. Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose from carbohydrates. It also promotes satiety, helping you maintain a healthy weight.
Incorporate healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, into your meals. These fats provide sustained energy and help prevent blood sugar fluctuations. However, consume them in moderation to avoid excessive calorie intake.
Fiber-rich foods, including fruits (especially berries), vegetables, and whole grains, are beneficial for individuals with insulinoma. Fiber slows down digestion, leading to a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. Additionally, it supports digestive health and can aid in weight management.
Rather than consuming three large meals a day, consider eating smaller, more frequent meals and snacks. This approach helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day and prevents the onset of hypoglycemic episodes.
Snacks that combine protein with a small amount of complex carbohydrates can be an excellent choice. For example, you might have a handful of almonds with a few whole-grain crackers or Greek yogurt with berries. These snacks provide sustained energy without causing rapid blood sugar spikes.
How do you care for a ferret with insulinoma?
In addition, ferrets with insulinoma should be fed many small meals throughout the day. A diet containing high quality protein and moderate levels of fat is preferred. Food with processed sugar or high levels of simple carbohydrates (such as fruit, semi moist cat food, cookies, etc.)
The journey of caring for a ferret with insulinoma begins with a visit to a veterinarian who specializes in exotic pets or ferrets. A proper diagnosis and assessment of the severity of the condition are crucial. Your veterinarian will recommend appropriate treatments, including medications and dietary changes.
Insulinoma in ferrets typically requires medication, such as prednisone or diazoxide, to manage blood sugar levels. Administer these medications as prescribed by your veterinarian. Regular visits are essential to monitor the ferret’s response to treatment and make necessary adjustments.
Diet plays a critical role in managing insulinoma. Modify your ferret’s diet to focus on foods that promote stable blood sugar levels. Prioritize high-quality ferret food with minimal carbohydrates and sugars. Lean proteins, such as poultry and fish, should be the primary component of their diet. Small, frequent meals throughout the day can help prevent hypoglycemic episodes.
Frequent monitoring of your ferret’s blood sugar levels is crucial. Work closely with your veterinarian to establish a monitoring schedule. This allows you to track the effectiveness of medication and dietary changes and make necessary adjustments promptly.
What can I give my ferret to raise blood sugar?
The current medication of choice for managing insulinoma is the steroid, prednisolone. Prednisolone helps the body make blood sugar but it also has many side effects. Eventually prednisolone alone is not enough to control signs of hypoglycemia, and a second drug, diazoxide may be added.
Honey or corn syrup can be effective for quickly raising a ferret’s blood sugar levels during a hypoglycemic episode. Offer a small amount (around half a teaspoon) on your finger or a spoon and allow them to lick it. Be cautious not to force-feed or use excessive amounts, as too much sugar can lead to other health issues.
Glucose gel is designed specifically for raising blood sugar levels and is available at most pet stores or through your veterinarian. Follow the dosage instructions provided with the product. It’s a convenient and safe option for immediate treatment.
These are high-calorie dietary supplements commonly recommended for ferrets. They contain sugars that can help elevate blood sugar levels. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate dosage and usage for your ferret.
Some commercial ferret treats are formulated to provide a quick energy boost. These often contain sugars or high-energy ingredients. Use them as a supplement to your ferret’s regular diet, especially during or after a hypoglycemic episode.
Can I give honey to ferret?
You can feed commercial ferret food or high-quality cat food. Dry food is recommended because a diet of soft food can lead to disease of the gums and digestion. Dairy foods, honey, raisins, and fruit should not be given to ferrets.
After providing honey to your ferret, closely monitor their response. Watch for any signs of improvement in their energy levels and symptoms. Be prepared to seek immediate veterinary care if their condition does not improve or worsens.
Before using honey or any other sugar-based products with your ferret, consult your veterinarian. They can provide specific guidance on the appropriate dosage and usage based on your ferret’s health status and individual needs.
While honey can temporarily raise blood sugar levels, it’s not necessarily the best option for managing insulinoma in ferrets. There are other products specifically designed for this purpose, such as glucose gels or high-calorie dietary supplements. These products are formulated for rapid blood sugar elevation and may be safer and more effective than honey.
It’s essential to remember that honey or any quick sugar source only provides temporary relief. To effectively manage insulinoma, the underlying condition must be addressed through a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include medication, dietary changes, and regular monitoring. Consult your veterinarian to develop such a plan.
Is insulinoma curable?
Most insulinomas are not cancer. A surgeon can usually remove it and cure the condition. This may be done using a laparoscope. In laparoscopy, the surgeon makes small incisions and uses special small tools to remove the tumor.
The primary approach to managing insulinoma in ferrets involves medication. Drugs like prednisone or diazoxide are commonly prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. These medications work by reducing insulin production and improving blood sugar stability. Ferrets with insulinoma usually require lifelong medication, and dosages may need to be adjusted periodically.
Diet plays a significant role in managing insulinoma. Feeding your ferret a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet can help prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Frequent, small meals are often recommended to maintain steady glucose levels throughout the day.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and your ferret’s overall condition is essential. Your veterinarian will you on how often these should occur. Adjustments to medication and diet can be made based on the results of these check-ups.
Ferrets with insulinoma can experience hypoglycemic episodes, which can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. Ferret owners must be prepared to administer quick sources of sugar (such as honey or glucose gel) and seek immediate veterinary care if needed.
Is sugar water good for ferrets?
Ferrets do not naturally get sugar in their diet and feeding foods high in sugar puts a tremendous strain on their pancreas. The result of sugar ingestion may lead to diabetes mellitus, which is extremely difficult to treat in the ferret and may ultimately leads to an early death.
Ferrets are obligate carnivores, meaning their natural diet consists primarily of animal-based proteins. Their bodies are adapted to efficiently process and utilize protein and fat for energy. Sugar, including the glucose found in sugar water, is not a significant part of their natural diet.
Ferrets are prone to a condition called insulinoma, where the pancreas overproduces insulin, leading to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). Giving sugar water to ferrets can lead to rapid increases in blood sugar levels, but this can be followed by a quick drop, potentially worsening their condition and symptoms.
The primary goal in managing insulinoma is to stabilize blood sugar levels to prevent hypoglycemic episodes. While sugar water might provide a short-term boost in blood sugar, it does not address the underlying issue and can even make it worse.
The best approach to managing insulinoma in ferrets is prevention. This involves providing a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet that helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Consult with your veterinarian to create an appropriate diet plan for your ferret’s specific needs.
How do you get rid of insulinoma?
Surgery is the preferred treatment for insulinoma. The location of the tumor is determined using diagnostic testing or surgical exploration. Single tumors are removed, but patients with multiple tumors usually require partial removal of the pancreas (partial pancreatectomy).
Diagnosing insulinoma in ferrets typically involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies. A veterinarian will look for symptoms such as lethargy, weakness, seizures, and changes in behavior. Confirmation usually requires blood tests to assess blood sugar levels and may include imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to visualize the pancreas.
The primary approach to managing insulinoma in ferrets involves medication. Drugs such as prednisone or diazoxide are commonly prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. These medications work by reducing insulin production and improving blood sugar stability. Ferrets with insulinoma usually require lifelong medication, and dosages may need to be adjusted periodically.
Diet plays a significant role in managing insulinoma. Feeding your ferret a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet can help prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Frequent, small meals throughout the day are often recommended to maintain stable glucose levels.
Ferrets with insulinoma can experience hypoglycemic episodes, which can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. Ferret owners must be prepared to administer quick sources of sugar (such as honey or glucose gel) and seek immediate veterinary care if needed.
Conclusion
The intricate world of ferret care, one cannot underestimate the proper nutrition, especially when dealing with a challenging condition like insulinoma. Managing ferrets insulinoma requires a holistic approach, and the foundation of this approach is a well-balanced diet. Throughout we’ve explored the key components of a ferret’s diet, focusing on carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. We’ve learned how to strike the right balance, avoiding high-sugar and high-carbohydrate foods while emphasizing protein-rich options to help stabilize blood sugar levels. Feeding frequency and portion sizes are critical considerations in managing insulinoma, as is the need for supplementation to ensure that your ferret is receiving all the essential nutrients.
Can create a tailored dietary plan that aligns with your ferret’s specific needs, ensuring they receive the nourishment required to combat insulinoma. Close monitoring of your pet’s condition, regular veterinary, and adjustments to their diet as needed are all essential components of managing insulinoma effectively. Collaboration with your veterinarian is crucial in this journey to provide the best possible care for your beloved ferret. Caring for a ferret with insulinoma is not without its challenges, but with dedication you can make a significant difference in their life.
Your ferret relies on you for their well-being, and by understanding their dietary needs and providing them with the right nutrition, you can help them thrive despite the challenges posed by insulinoma. As you embark on this path of nutritional care, remember that the bond you share with your ferret is a powerful motivator. Your commitment to their health, coupled with the insights gained from it can lead to a happier, healthier, and longer life for your ferret with insulinoma. With love, patience, and the right diet, you can be the light that helps your ferret navigate the complexities of this condition and enjoy a fulfilling life by your side.





No Comments