Introduction
How Many Babies Can A Rat Have: Rats, those ubiquitous rodents that often scurry through urban alleyways and make unwelcome appearances in our homes, have long been subjects of curiosity and even fascination. This seemingly simple query belies the fascinating world of rat reproduction and the remarkable capacity of these animals to multiply. Rats food belong to the order Rodentia, a group of mammals renowned for their prolific breeding habits. Within this order, the brown rat, also known as the Norway rat, and the black rat are among the most notorious species due to their association with human settlements. Their presence may often be unwelcome, understanding the intricacies of rat reproduction can shed light on these creatures have become such successful urban inhabitants.
The reproductive capabilities of rats are nothing short of astonishing. Female rats, or does, are known for their exceptional fertility and short gestation periods, which contribute to their ability to rapidly increase their population. A single female rat can potentially give birth to a large number of offspring in a relatively short period. This prolific breeding capability has earned rats a reputation for being among the most successful and adaptable mammals on Earth, thriving in diverse environments across the globe.
The factors that influence the number of babies a rat can have, the mechanisms of their reproductive cycles, and the implications of their prolific breeding on both natural ecosystems and urban environments. By understanding the intricacies of rat reproduction, we can gain insights into their remarkable adaptability and learn how to manage their populations more effectively when necessary. Where we unravel the mysteries of their reproductive prowess and discover that rat babies are more intriguing than it may initially seem.
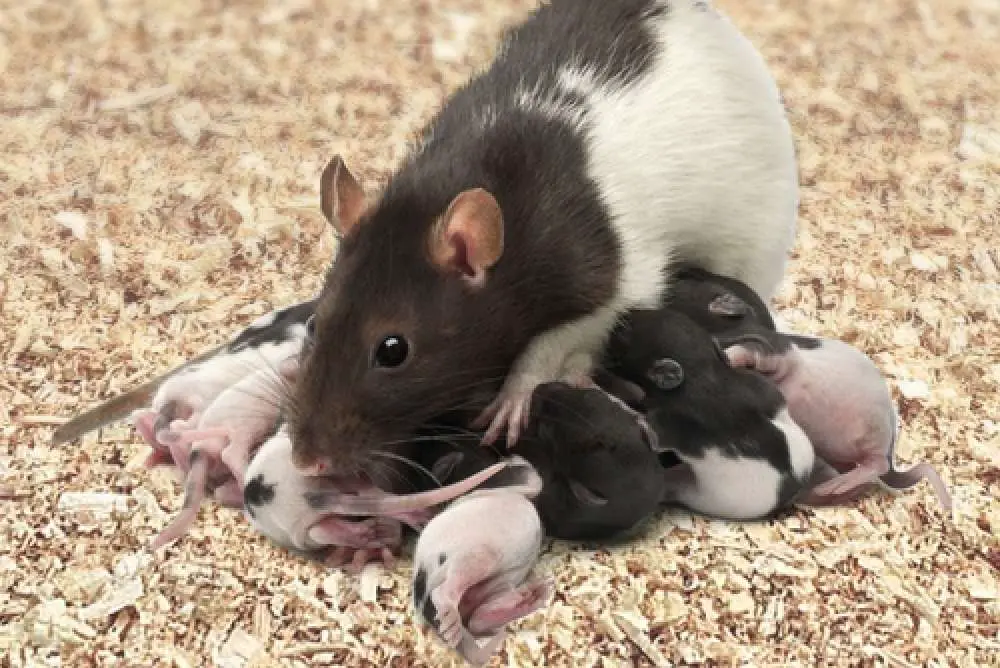

How quickly do rats multiply?
A female rat typically births six litters a year consisting of up to 12 rat pups, although 5-10 pups are more common. Rats reach sexual maturity after nine weeks, meaning that a population can swell from two rats to around 1,250 in one year, with the potential to grow exponentially.
The reproductive capacity of rats, particularly the brown rat and the black rat, is a testament to their biological resilience. Female rats, or does, possess a remarkable fertility rate, with the ability to produce several litters of pups each year. This fertility, combined with short gestation periods and a relatively rapid maturation process, allows rats to multiply rapidly.
Environmental factors play a pivotal role in influencing the rate at which rats multiply. Urban environments, with their abundant food sources, shelter options, and temperature-controlled settings, often the ideal conditions for rats to thrive and reproduce. This makes cities and human settlements particularly susceptible to rat infestations, necessitating effective pest management strategies.
The exponential growth of rat populations highlights the importance of proactive measures to control and mitigate rat infestations. Left unchecked, a small rat population can quickly burgeon into a significant problem, leading to various issues such as property damage, health concerns, and disruptions to ecosystems.
How many babies can a pet rat have?
Rats are a very prolific species and one female can have up to twenty babies in one litter. The gestation period for rats is about twenty days, so you can expect to see the babies around three weeks after mating.
Genetics: The lineage of the pet rat plays a role in determining litter size. Rats bred for show or specific traits might have different reproductive characteristics than rats from less controlled breeding.
Age: Younger does may have smaller litters initially, and their reproductive capacity tends to increase as they mature. Rats typically reach sexual maturity at around 5-6 weeks of age, but it is advisable to wait until they are at least 3-4 months old before breeding them.
Health: The health and well-being of the doe significantly impact her ability to reproduce. Proper nutrition and regular veterinary care are essential to ensure that the doe can have healthy litters.
Environment: Unlike their wild counterparts, pet rats live in controlled environments where factors like food availability and temperature are consistent. This can contribute to more reliable and steady reproduction rates.
Can a 2 year old rat get pregnant?
You can’t count on a female being completely infertile until she is 2 years old. Before deciding to breed your rats, you should consider a few things. Do not breed rats who have or have had active mycoplasma infections.
Reproductive Lifespan: Rats, both in the wild and as pets, have a finite reproductive lifespan. Typically, female rats are most fertile and capable of reproducing between the ages of 5 weeks to 1 year, with their peak fertility occurring around 3 to 6 months of age. After this period, their fertility begins to decline.
Senescence: As female rats age, they undergo a process called reproductive senescence. This means that their reproductive organs and systems start to function less efficiently. By the time a rat reaches 2 years of age, she is well past her prime reproductive years, and her chances of successfully conceiving and carrying a litter to term are extremely low.
Health Concerns: Aging rats may also face various health issues that can further reduce their ability to conceive and carry offspring. These health concerns can include problems with their reproductive organs, such as uterine tumors or infections, which can hinder fertility.
Social Considerations: In a pet rat’s social environment, it’s consider the well-being of both the mother and any potential offspring. Breeding an older rat can place stress on her body and increase the risks associated with pregnancy and birth.
At what age can a rat get pregnant?
In the laboratory, the traditional breeding age of rats begins at 3-4 months and ends at 10-12 months of age. Male rats are capable of impregnating females as early as 5 weeks of age, although this is not common.
Puberty and Sexual Maturity: Female rats typically reach sexual maturity and become capable of getting pregnant around 5 to 6 weeks of age. However, it’s essential to note that just because a rat can become pregnant at this age does not mean it’s advisable. Rats are still quite small and may not be physically or emotionally prepared for pregnancy and motherhood at such a young age.
Optimal Age for Breeding: Rats can technically become pregnant at around 5 weeks, it is generally to wait until they are at least 3 to 4 months old before considering breeding them. Breeding younger rats can lead to complications and increased health risks for both the mother and the offspring. Waiting until the rats are a few months old allows them to mature physically and emotionally, making them better equipped to handle the demands of pregnancy and raising a litter.
Environmental Factors: The age at which a rat becomes pregnant can be influenced by environmental factors such as diet and living conditions. Rats in optimal health with a balanced diet are more likely to reach sexual maturity and become pregnant at the lower end of the age range.
Where do rats sleep?
Yes, many species of rats make nests as a place to hide and sleep. A rat’s nest is also a place for them to store food scavenged from your home. Pregnant rats usually give birth to their babies in nests and leave them there when they go out looking for water and food.
Burrows: Many wild rat species, such as the brown rat and the black rat, are burrowing animals. They create complex underground burrows that serve as their primary homes. These burrows shelter from predators, protection from the elements, and a safe place to sleep.
Nests: Within their burrows, wild rats construct nests made of materials like leaves, grass, and shredded paper. These nests serve as cozy sleeping quarters where rats can rest and raise their young.
Hidden Spots: Wild rats are nocturnal and are known for their secretive behavior. During the day, they often sleep in hidden or protected spots within their burrows or in secure, dark locations away from predators.
Cages: Domesticated or pet rats typically live in cages or enclosures by their owners. Inside these cages, they have designated sleeping areas that often consist of cozy bedding materials like shredded paper, cloth, or fleece. Owners often small hideaways, hammocks, or nest boxes where their pet rats can sleep comfortably.
What do baby rats eat?
What Do Baby Rats Eat? Newborn baby rats drink their mother’s milk for around three weeks. After that, they can eat solid food but may continue to nurse for several more weeks while they learn about other foods. Baby rats then transition into an adult diet.
For the first few days of their lives, baby rats rely entirely on their mother’s milk. The mother rat’s milk, often referred to as colostrum, is rich in essential nutrients, antibodies, and growth factors crucial for the pups’ health and development.
Baby rats begin to transition to solid food when they are around 2 to 3 weeks old. This process, called weaning, involves gradually introducing solid foods while still nursing from their mother. During this phase, the mother rat may regurgitate partially digested food for the pups to consume, aiding in their transition to solid foods.
As baby rats grow and become more independent, they start to consume soft solid foods. These foods should be easily chewed and digested. Specialized rat pellets or blocks designed for all life stages can be moistened with water to create a soft texture that baby rats can eat. Unsweetened, iron-fortified baby cereals mixed with water to create a porridge-like consistency are suitable for young rats.
How do I know if a rat is pregnant?
The average gestation time is 21 to 23 days, and pregnancy is sometimes detectable at about 2 weeks by feeling the abdomen or noticing weight gain or mammary (breast) development. Pregnant females will make a nest, and they should be with suitable materials.
Pregnant rats often exhibit nesting behavior. They may become more active in building or rearranging their nests using bedding materials to create a cozy, secure space for giving birth and raising their young.
Gentle palpation of the rat’s abdomen can sometimes help identify pregnancy. You may be able to feel small lumps or masses within the abdomen, which could indicate the presence of developing fetuses. However, this should be done very carefully and preferably by a veterinarian or an experienced rat owner to avoid harming the rat or causing stress.
If you want a definitive confirmation of pregnancy, you can consult with a veterinarian who can perform an ultrasound or X-ray to visualize the presence of developing fetuses. This is the most accurate way to determine pregnancy.
How many months are rats pregnant?
The average gestation time is 21 to 23 days, and pregnancy is sometimes detectable at about 2 weeks by feeling the abdomen or noticing weight gain or mammary (breast) development.
Gestation Period: The typical gestation period for rats is approximately 21 to 23 days, with some variation depending on factors such as the rat’s age, health, and environmental conditions.
Early Detection: It can be challenging to detect pregnancy in rats during the early stages because physical changes are not always obvious. However, some behavioral and physical indicators may become more apparent as the pregnancy progresses.
Behavioral Changes: As the pregnancy nears its end, pregnant rats often exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased nesting activity and restlessness. These behaviors are signs that the rat is preparing for labor and birth.
Nesting: Pregnant rats tend to become more active in building or enhancing their nests in preparation for giving birth. They use bedding materials to create a secure and comfortable environment for their offspring.

Conclusion
In babies a rat can open a window into the fascinating world of rat reproduction and the remarkable adaptability of these creatures. Rats, particularly the brown rat and the black rats babies, are known for their astonishing fertility and rapid population growth. Through an understanding of the factors that influence rat reproduction. Firstly, female rats, or does, exhibit an exceptional ability to reproduce quickly due to their high fertility rates and short gestation periods. A single female rat can potentially give birth to dozens of offspring within a year, and this prolific breeding capability has contributed to their success as urban inhabitants.
The environment plays a significant role in determining the reproductive success of rats. Factors such as food availability, shelter, and temperature can impact their breeding patterns. Urban environments, with their abundance of resources and hiding places, often ideal conditions for rats to thrive and reproduce. Rat reproduction is not just a matter of curiosity but has implications for pest control and conservation efforts. In urban settings, effective rat population management is crucial to mitigate the potential health risks and property damage associated with rat infestations.
In babies a rat can have, we’ve touched upon the broader issues of coexistence between humans and rats. Rats may be viewed as pests in urban areas, they also deserve study and respect for their remarkable adaptability and survival strategies. By gaining insights into rat reproduction, we can develop more effective strategies for managing rat populations and minimizing the conflicts that arise between humans and these resilient rodents. They serve as a reminder that even in the most challenging environments, nature finds a way to persist and thrive.




No Comments